Explain the Different Stages of Soil Formation
Stages of group development diagram. Soil formation can be a dry topic for students in science classes.

How Is Soil Formed From Parent Material Quora
These horizons are often present in.
. The partial decomposition is due to the accumulation of the matter underwater which cuts off the oxygen supply. This is the second stage in the coal formation. Iii Translocation of mineral and organic matter from one point of soil profile and deposited at another horizon.
Mohr and Van Barren have recognized five stages in the development of soils in relation to time. Stages of Soil Formation. The Adjourning Stage mainly characterized by a sense of closure.
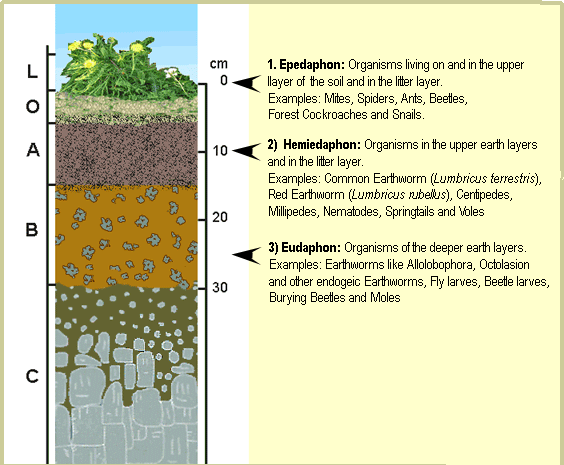
Animals and micro-organisms mix soils and form burrows and pores. Plants animals micro-organisms and humans affect soil formation. Soil broadly consists of four layers.
Deposition is the accumulation of new materials that have been eroded from another place such as river gravels or blown gravel or the creation of new rocks. The Norming Stage mainly characterized by cooperation integration and unity. Different types of roots have different effects on soils.
Soil Formation Surface And Groundwater Weathering and Soils. Terms in this set 6 The rock weathers. The formation of true soil from Regolith The evolution of true soil from regolith takes place by the combined action of.
If a single parent material is exposed to different climates then a different soil individual will form. Making the lesson hands-on is an important step in helping students understand the many processes that go on. Topography which modifies the water relationship in soils and to a considerable extent influences soil erosion is usually treated as a soil former.
This is the outer thin layer. 1 Addition of mineral and organic matter to the soil. This is the first stage in the formation of coal.
The whole soil from the surface to its lowest depths develops naturally as a result of these five factors. A fourth factor of soil formation is the configuration of the landscape. Ii Losses of mineral and organic matter from soil.
1 parent material 2 relief or topography 3 organisms including humans 4 climate and 5 time. Animals such as insects and worms start to appear. Everything takes a very long time indeed.
Plant roots open channels in the soils. This layer lies below the top soil. 1 Nudation 2 Migration 3 Germination 4 Ecesis 5 Colonisation and Aggregation 6 Competition and Co-action 7 Invasion 8 Reaction and 9 Stabilisation.
The weathering of rock R into Regolith 2. Soils have 6 major horizontal layers or horizons that can be present. He left the in case there were other factors that he had not considered at the time.
The soil formation process depends upon the presence of new soil material which is either acquired by denudation or deposition. Ie the topography of the. It is an organic substance which is formed due to the partial decomposition of dead matter.
Weathering just started but much of the original material is still un-weathered. R relief or topography p parent material. The document has moved here.
S soil formation. Time is perhaps the most important factor when it comes to soil formation. Grass roots are fibrous near the soil surface and easily decompose adding organic matter.
The Performing Stage mainly characterized by overall synergy. The Storming Stage mainly characterized by a power struggle. The hydrosere is a continuum of vegetation types that replace each other as habitat succession proceeds from an initial phase open water or other to bog in response to changes in water depth trophic status and plant communities.
It contains fine particles and organic matter. It is on this layer that plants and crops grow. The process of plant succession consists of nine steps.
The fundamental process of soil formation are the following. Denudation is the abrasion of present rock material by the action of ice water or wind. Soil and soil formation can.
This layer lies below the sub soil. First Stage Peat. 2 Losses of mineral and organic matter from soil.
The nine steps are. 3 Translocation of mineral and organic matter from one point of soil profile and deposited at another horizon. Easily weatherable minerals have been decomposed for the greater part.
I Addition of mineral and organic matter to the soil. Soil formation is a process strongly driven by the boundary conditions. The fundamental process of soil formation are as follows.
Soil formation factors and processes The soil formation is the process of two consecutive stages. The soil formation process begins with a parent material that determines the mineral composition and widely contributes to the chemical and physical properties of the soil. The plants begin to grow.
The hydrosere may be initiated in waters of any trophic status from oligotrophic to eutrophic followed by infilling of the water. Second Stage Lignite. Like humans soils have different properties based on where they are from and where they grew up formed.
It contains materials which are removed from the top soil. Soil Formation Processes details how new soil can appear in a new location and how soil looks change over time. There are several ways or mechanisms involved in soil formation.
It is in first stage of soil formation. The five factors are.
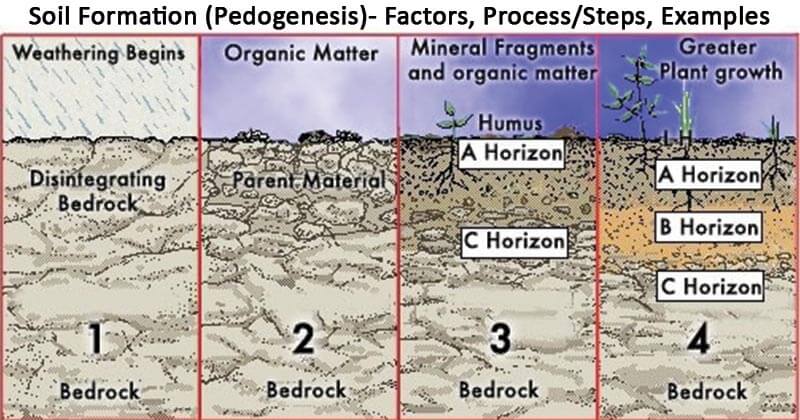
Soil Formation Pedogenesis Factors Process Steps Examples

How Soils Form Environment Land And Water Queensland Government
Comments
Post a Comment